Determina l'area di un triangolo rettangolo sapendo che l'ipotenusa misura
[math]45m[/math]
e la somma dei cateti è
[math]63m[/math]
.
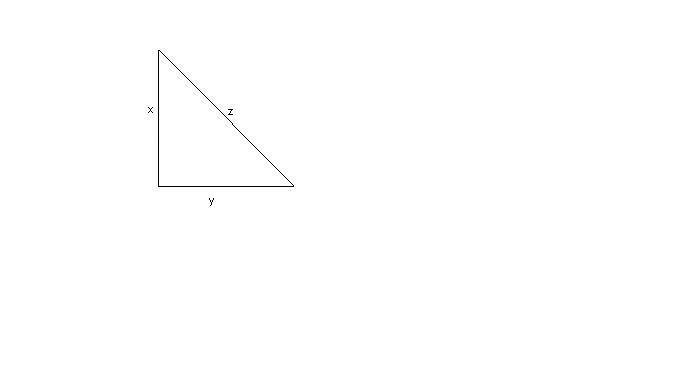
Svolgimento
Indicando con
[math]x[/math]
e
[math]y[/math]
i due cateti e con
[math]z[/math]
l'ipotenusa, i dati sono:
[math]x+y=63m ^^ z=45m[/math]
Per il teorema di
Pitagora sappiamo che
[math]z=\sqrt{x^2+y^2} => \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=45m[/math]
.
Mettiamo a sistema le due
equazioni e procediamo nella risoluzione
[math]\begin{cases} \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=45 \\ x+y=63 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=45 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
Eleviamo al quadrato ambo i membri della prima equazione e procediamo per sostituzione
[math]\begin{cases} x^2+y^2=2025 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} (63-y)^2+y^2=2025 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} 3969-126y+y^2+y^2=2025 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
Semplificando
[math]\begin{cases} 2y^2-126y+1944=0 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
Dividendo la prima equazione per
[math]2[/math]
si ha:
[math]\begin{cases} y^2-63y+972=0 \\ x=63-y \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
Risolviamo l'equazione di secondo grado
[math]y^2-63y+972=0[/math]
[math]Delta=b^2-4ac=(-63)^2-(4 \cdot (972) \cdot 1)=3969-3888=81[/math]
[math]y_(1,2)=(-b+-\sqrt{Delta})/(2a)=(63+-\sqrt(81))/2=(63+-9)/2 => y_1=36 ^^ y_2=27[/math]
.
Pertanto
[math]\begin{cases} y_1=36 \\ x_1=63-y_1 \ \end{cases} => {(y_1=36),(x_1=27):}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} y_2=27 \\ x_2=63-y_2 \ \end{cases} => {(y_2=27),(x_2=36):}[/math]
.
Le misure dei cateti sono
[math]27m[/math]
e
[math]36m[/math]
Pertanto
[math]A=(x \cdot y)/2=((27) \cdot (36))/2m^2=486m^2[/math]
.








 Accedi a tutti gli appunti
Accedi a tutti gli appunti
 Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo
Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo