Scrivere l'equazione della retta
[math]r[/math]
passante per il punto
[math](2/3;-1)[/math]
e di
coefficiente angolare[math]-3[/math]
.
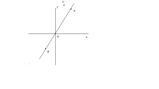
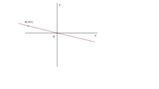
Disegnare la retta ottenuta.
Svolgimento
L'equazione
[math]y-y_0=m(x-x_0)[/math]
rappresenta la retta passante per il punto
[math](x_0;y_0)[/math]
e avente un assegnato coefficiente angolare
[math]m[/math]
.
Nel nostro caso
[math]x_0=2/3, y_0=-1, m=-3[/math]
Sostituendo nell'equazione generale si ha:
[math]y+1=-3(x-2/3)[/math]
;
sviluppando e raccogliendo i termini simili
[math]y+1=-3x+2[/math]
;
[math]y=-3x+1[/math]
.
Quest'ultima equazione rappresenta la retta passante per il punto
[math](2/3;-1)[/math]
e di coefficiente angolare
[math]-3[/math]
.
Per rappresentarla graficamente basta intersecare la retta con gli assi
[math]\begin{cases} y=-3x+1 \\ x=0 \ \end{cases} => {(y=1),(x=0):}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} y=-3x+1 \\ y=0 \ \end{cases} => {(x=1/3),(y=0):}[/math]
.









 Accedi a tutti gli appunti
Accedi a tutti gli appunti
 Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo
Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo