[math]|3x+2|>x-5[/math]
Per risolvere la disequazione dobbiamo distinguere il caso in cui l'espressione
[math]3x+2[/math]
è positiva o nulla da quello in cui è negativa. Infatti
Se
[math]3x+2>=0[/math]
la disequazione è equivalente a
[math]3x+2>x-5[/math]
Se
[math]3x+2>0[/math]
la disequazione è equivalente a
[math]3x+2> -x+5[/math]
In definitiva, per risolvere la disequazione data, dobbiamo risolvere i due sistemi
[math]\begin{cases} 3x+2>=0 \\ 3x+2>x-5 \ \end{cases} vv {(3x+2>0),(3x+2> -x+5):}[/math]
;
Studiamo il primo sistema
[math]\begin{cases} 3x+2>=0 \\ 3x+2>x-5 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} 3x>=-2 \\ 2x>-7 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} x>=-2/3 \\ x>-7/2 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;

Pertanto
[math]S_1=x>=-2/3[/math]
Studiamo ora il secondo sistema
[math]\begin{cases} 3x+2>0 \\ 3x+2> -x+5 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} 3x>-2 \\ 4x>3 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} x>-2/3 \\ x>3/4 \ \end{cases}[/math]
;
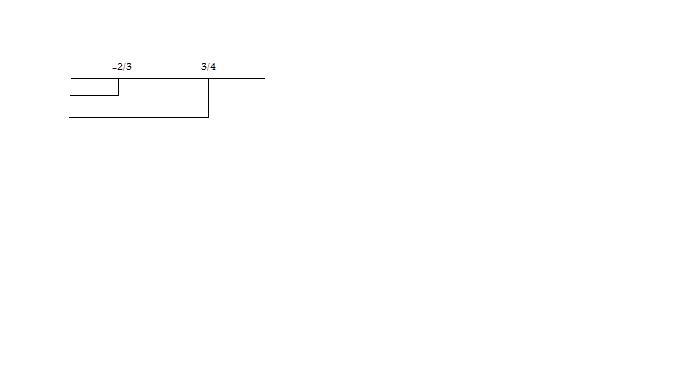
Pertanto
[math]S_2=x>-2/3[/math]
In definitiva quindi la soluzione è data dalle unioni delle due soluzioni, cioè:
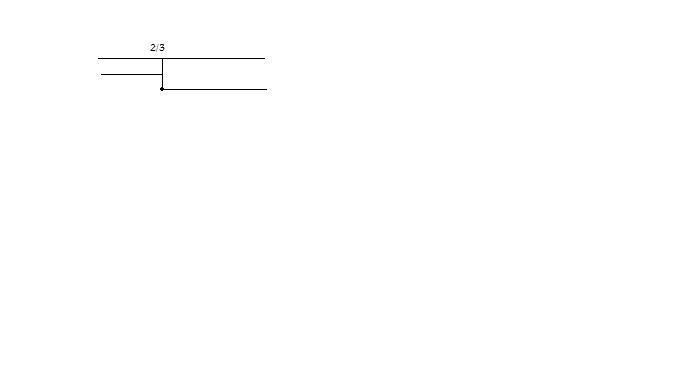
[math]S=S_1 uu S_2 : x_1>-2/3 ^^ x_2> -2/3 => S=RR[/math]
.

 Pertanto
Pertanto 









 Accedi a tutti gli appunti
Accedi a tutti gli appunti
 Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo
Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo