Scrivere l'equazione della retta passante per i punti
[math](1;-2/3)[/math]
e [math](6;1)[/math]
e rappresentarla graficamente. Svolgimento
Indichiamo con
[math]A[/math]
e [math]B[/math]
rispettivamente i punti di coordinate [math](1;-2/3)[/math]
e [math](6;1)[/math]
.La retta
[math]r[/math]
non è parallela ad alcun asse, poichè [math]x_2!=x_1[/math]
e [math]y_2!=y_1[/math]
, e quindi la sua equazione avrà la forma:[math]y=mx+q[/math]
con [math]m[/math]
e [math]q[/math]
coefficienti da determinare.Dobbiamo imporre che le coordinate di
[math]A[/math]
e [math]B[/math]
verifichino l'equazione [math]y=mx+q[/math]
.Se
[math]A(1;-2/3) in r => -2/3=m \cdot 1+q => -2/3=m+q[/math]
.Se
[math]B(6;1) in r => 1=6m+q[/math]
.Mettiamo a sistema le due equazioni e risolviamolo
[math]\begin{cases} -2/3=m+q \\ 1=6m+q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} -2/3=m+q \\ 1-6m=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} -2/3=m+1-6m \\ 1-6m=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
; [math]\begin{cases} -2/3-1=-5m \\ 1-6m=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} (-2-3)/3=-5m \\ 1-6m=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
; [math]\begin{cases} -5/3=-5m \\ 1-6m=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} 1/3=m \\ 1-6 \cdot 1/3=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
; [math]\begin{cases} 1/3=m \\ 1-2=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} 1/3=m \\ -1=q \ \end{cases}[/math]
;Pertanto l'equazione della retta
[math]r[/math]
passante per [math]A[/math]
e [math]B[/math]
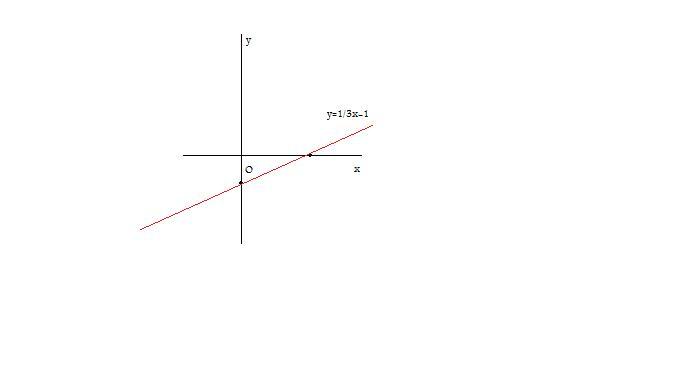
sarà:[math]y=1/3x-1[/math]
Per rappresentarla graficamente basta intersecare la retta con gli assi
[math]\begin{cases} y=1/3x-1 \\ x=0 \ \end{cases} => {(y=-1),(x=0):}[/math]
;[math]\begin{cases} y=1/3x-1 \\ y=0 \ \end{cases} => {(1=1/3x),(y=0):} => {(3=x),(y=0):}[/math]
.







 Accedi a tutti gli appunti
Accedi a tutti gli appunti
 Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo
Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo