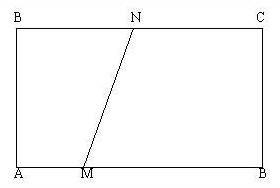
Il perimetro del rettangolo
[math]ABCD[/math]
è
[math]50cm[/math]
, la base
[math]\bar(AB)=20cm[/math]
.
Determinare un punto
[math]M[/math]
sul lato
[math]\bar(AB)[/math]
e un punto
[math]N[/math]
sul lato
[math]\bar(CD)[/math]
in modo che
[math]\bar(NC)=2\bar(AM)[/math]
e che
l'area del trapezio
[math]MBCN[/math]
sia di
[math]65cm^2[/math]
.Calcolare la misura di
[math]\bar(AM)[/math]
.
 Dati
Dati
[math]2p=50cm[/math]
[math]A_(MBCN)=65cm^2[/math]
[math]\bar(AB)=20cm[/math]
[math]\bar(NC)=2\bar(AM)[/math]
Svolgimento
Indichiamo
[math]\bar(AM)=x[/math]
, quindi
[math]\bar(MB)=20cm-x[/math]
e
[math]\bar(NC)=2x[/math]
Conoscendo il perimetro del rettangolo e la misura di una base possiamo calcolare la misura di
[math]\bar(CB)[/math]
[math]\bar(CB)=(2p-(\bar(AB)+\bar(DC)))/2=(50-40)/2cm=5cm[/math]
.
[math]A_(MBCN)=65cm^2[/math]
, cioè
[math](\bar(MB)+\bar(NC))/2(\bar(CB))=65cm^2[/math]
Sostituendo si ha
[math](20-x+2x)/2 \cdot 5=65[/math]
Risolvendo questa equazione di primo grado troveremo il valore di
[math]x[/math]
e quindi la misura di
[math]AM[/math]
[math](20-x+2x)/2 \cdot 5=65[/math]
;
semplificando
[math](20+x)/2=13[/math]
;
[math](20+x)=26[/math]
;
[math]x=26-20 -> x=6[/math]
Pertanto
[math]\bar(AM)=6cm[/math]
.
 Dati
Dati








 Accedi a tutti gli appunti
Accedi a tutti gli appunti
 Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo
Tutor AI: studia meglio e in meno tempo