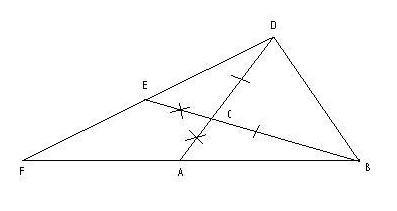
Sia
[math]hat{ABC}[/math]
un triangolo qualsiasi, prolunghiamo
[math]\bar(AC)[/math]
e su di essa
consideriamo
[math]D[/math]
tale che
[math]\bar(CD)~=\bar(CB)[/math]
; prolunghiamo anche
[math]\bar(CB)[/math]
e su di essa consideriamo
[math]E[/math]
tale che
[math]\bar(CE)~=\bar(CA)[/math]
.
Le rette
[math]DE[/math]
e
[math]AB[/math]
si incontrano in
[math]F[/math]
. Dimostrare che
[math]hat{DFB}[/math]
è isoscele.
 Ipotesi
Ipotesi
[math]\bar(CD)~=\bar(CB)[/math]
[math]\bar(CE)~=\bar(CA)[/math]
Dimostrazione
sappiamo che
[math]ChatDB~=ChatBD[/math]
perchè è isoscele il triangolo
[math]hat{CDB}[/math]
.
Inoltre
[math]hat{ECD}~=hat{ACB}[/math]
per il primo criterio di uguaglianza, infatti
[math]\bar(EC)~=\bar(AC)[/math]
per ipotesi
[math]\bar(CD)~=\bar(CB)[/math]
per ipotesi
[math]EhatCD~=AhatCB[/math]
perchè opposti al vertice
Di conseguenza
[math]EhatDC~=AhatBC[/math]
.
Si può concludere che
[math]FhatDB~=FhatBD[/math]
, perchè somma di angoli congruenti, precisamente
[math]FhatDB=FhatDC+ChatDB[/math]
e
[math]FhatBD=FhatBE+EhatBD[/math]
,
con
[math]FhatDC=FhatBE[/math]
e
[math]ChatDB=EhatBD[/math]
; e quindi poichè un triangolo che ha due angoli uguali
ha anche uguali i lati opposti a questi è isoscele, concludiamo che
[math]hat{DFB}[/math]
è isoscele.
 Ipotesi
Ipotesi Ipotesi
Ipotesi